IDE storage device
All our storage devices such as hard disk, CD/DVDs are called IDE because electronic circuitry required for these devices to function are already integrated into them.
Hard disk
Physical Structure of a Hard disk
-Inside the Hard disk we can find metal disc’s called platters. These platters store all or our data. Data is stored separately on both sides of platter (Top and Bottom).
-The R/W heads store data into the platter. Each platter has 2 R/W heads one for the top and other for the bottom.
-According to the total capacity of the hard disk it can have 2 or more platters.
-Each platter is divided into logical ring called Tracks. These tracks are further divided into small setions called sectors.
-All data saved in the hard disk is saved into these sectors. Each sector can hold up to 512bytes of data.
Partitions (Drives)
-Before using the hard disk e need to first create partitions and then format.
-Partitioning means to divide a single hard disk into multiple logical pieces for easy storage of our data. At least one partition must be created.
-Partitions can be created according to type and sizes.
-the following types of partitions can be created:
1. Primary Partition:
-This is the first and main drive ( c: )
-For operating system to be installed and booted at least one partition is required.
-Up to 4 primary partitions cab be created.
2. Extended partition.
-This is more of a storage container than actually a drive. It is used to store logical drive.
-Using logical drives we can create up to 24 drives. (d: e: f: ……z: )
3. Logical Drives
-These are the drives created inside the extended partition.
Dynamic Volumes
-If we want we can convert our hard drive to dynamic disk.
-using this we can create dynamic volumes such as;
1. Simple volume
-This is the same as primary or logical drive.
2. Spanned volume
-This can be used to connect free spaces of up to 32 hard disks and crate a single drive.
3. Mirrored volume
-This is mainly used for creating a backup copy of the primary drive into a drive located in the second hard disk. In case the first hard disk is damage we can use the second hard disk to start the computer.
4. Striped volumes.
-this can be created suing 3 to 32 harddisks.
-The striped volumes provide faster read/write performance compared to other drivews.
-When we save files into a striped volume it is divided into pieces and each pieces is saved into a separate drive, this makes saving faster.
-and when we open files all drives together open the files, making reading process faster.
- But if a single hard drive were to fail then all data will be lost.
5. Stripped with parity.
-This is the same as striped but it also provides fault tolerance.
-if a single hard disks fails then it can be replaced with a new one and all data can be restored.
Formatting
-After creating drives we need to format each drives.
- formatting will create a file system table which stores information about which files are stored in which tracks and sectors of the hard disk.
-the following types of file system are available;
1) FAT: File Allocation Table 16
- This is the oldest type of file system used mainly in Windows 95 and Windows 98.
-This supports maximum drive size of up to 2.1 GB.
-Now a days this is only used for pen-drives or memory card.
2) FAT32
-This is the advancement of FAT16
-It can support maximum drive size of up to 32GB.
3) NTFS
-This is the currently used file system.
-It has many advantages compared to FAT file system.
-It can support maximum drive size of upto 2 Terabytes.
-Also it has many extra features such as ;
a. compression
b. encryption
c. NTFS file/folder permission
d. Disk Quota
All our storage devices such as hard disk, CD/DVDs are called IDE because electronic circuitry required for these devices to function are already integrated into them.
Hard disk
Physical Structure of a Hard disk
-Inside the Hard disk we can find metal disc’s called platters. These platters store all or our data. Data is stored separately on both sides of platter (Top and Bottom).
-The R/W heads store data into the platter. Each platter has 2 R/W heads one for the top and other for the bottom.
-According to the total capacity of the hard disk it can have 2 or more platters.
-Each platter is divided into logical ring called Tracks. These tracks are further divided into small setions called sectors.
-All data saved in the hard disk is saved into these sectors. Each sector can hold up to 512bytes of data.
Partitions (Drives)
-Before using the hard disk e need to first create partitions and then format.
-Partitioning means to divide a single hard disk into multiple logical pieces for easy storage of our data. At least one partition must be created.
-Partitions can be created according to type and sizes.
-the following types of partitions can be created:
1. Primary Partition:
-This is the first and main drive ( c: )
-For operating system to be installed and booted at least one partition is required.
-Up to 4 primary partitions cab be created.
2. Extended partition.
-This is more of a storage container than actually a drive. It is used to store logical drive.
-Using logical drives we can create up to 24 drives. (d: e: f: ……z: )
3. Logical Drives
-These are the drives created inside the extended partition.
Dynamic Volumes
-If we want we can convert our hard drive to dynamic disk.
-using this we can create dynamic volumes such as;
1. Simple volume
-This is the same as primary or logical drive.
2. Spanned volume
-This can be used to connect free spaces of up to 32 hard disks and crate a single drive.
3. Mirrored volume
-This is mainly used for creating a backup copy of the primary drive into a drive located in the second hard disk. In case the first hard disk is damage we can use the second hard disk to start the computer.
4. Striped volumes.
-this can be created suing 3 to 32 harddisks.
-The striped volumes provide faster read/write performance compared to other drivews.
-When we save files into a striped volume it is divided into pieces and each pieces is saved into a separate drive, this makes saving faster.
-and when we open files all drives together open the files, making reading process faster.
- But if a single hard drive were to fail then all data will be lost.
5. Stripped with parity.
-This is the same as striped but it also provides fault tolerance.
-if a single hard disks fails then it can be replaced with a new one and all data can be restored.
Formatting
-After creating drives we need to format each drives.
- formatting will create a file system table which stores information about which files are stored in which tracks and sectors of the hard disk.
-the following types of file system are available;
1) FAT: File Allocation Table 16
- This is the oldest type of file system used mainly in Windows 95 and Windows 98.
-This supports maximum drive size of up to 2.1 GB.
-Now a days this is only used for pen-drives or memory card.
2) FAT32
-This is the advancement of FAT16
-It can support maximum drive size of up to 32GB.
3) NTFS
-This is the currently used file system.
-It has many advantages compared to FAT file system.
-It can support maximum drive size of upto 2 Terabytes.
-Also it has many extra features such as ;
a. compression
b. encryption
c. NTFS file/folder permission
d. Disk Quota
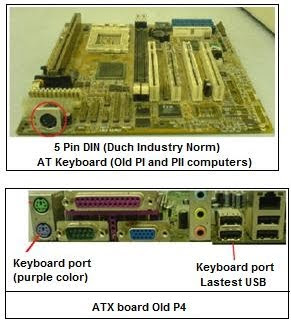
 -AT motherboards uses the P8 and P9 power connector
-AT motherboards uses the P8 and P9 power connector -ATX motherboard uses P1 power connectors and P4 power connector.
-ATX motherboard uses P1 power connectors and P4 power connector. -For PATA drives we need to connect white Molex connector.
-For PATA drives we need to connect white Molex connector. -For SATA drives we need to connect black Molex connector.
-For SATA drives we need to connect black Molex connector.  -used to supply power to floppy drives.
-used to supply power to floppy drives.