Coaxial cable (RG-8/ RG-58)
Twisted Pair Cable (UTP/STP)
Fiber Optic
1. Coaxial cable (RG-8/ RG-58)
There are 2 types of coaxial cables, RG-8 (Thick Net) and RG-58(Thin Net). These were used in physical Bus network.
RG-8:
It had a thick outer coating and was resistant to EMI.
But it was difficult to setup because the outer coating made it less flexible.
It used the AUI connector.
It could support 100 computers and Max distance of 500 meters.
RG-58:
It had a thinner outer coating which made it flexible and easier to setup.
It used the BNC connector.
It can support 30 computers and maximum distance of 185 meters.
2. Twisted Pair Cable (UTP/STP)
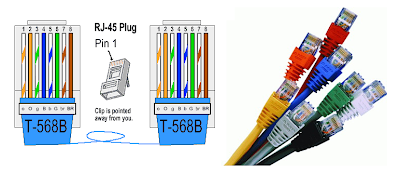
These are the commonly used cables in networking.
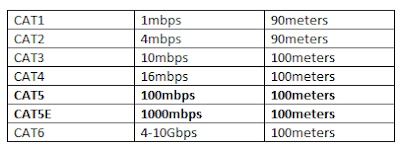
T.P cables come in different category and each category supports a different speed and distance. There can be 1, 2, or 4 pairs of cables according to category.
3. Fiber Optic
This is a advanced type of cable which transfers data in form of light signals.
Light signals support much higher distances and speeds. Also light signals are completely immune toward EMI.
It is mainly used for long distance connections.
It is very used for long distance connections.
It is very expensive and difficult to handle. We required special training to be able to handle these cable.
Max distance 500meters.
(Note: no interference 100% guaranteed)






